- 8 Mart 2021
- 5181 defa okundu.
Honorable Mention, The Urban Adaptation Competition
Onur Karataş, Alp Fahri Ardıç ve Muhammed Yasin Gülmez ekibinin Modu-Rot isimli projesi, MetsaWood'un düzenlediği uluslararası "Urban Adaptation" yarışmasında "Honourable Mention" ödülüne layık görüldü.
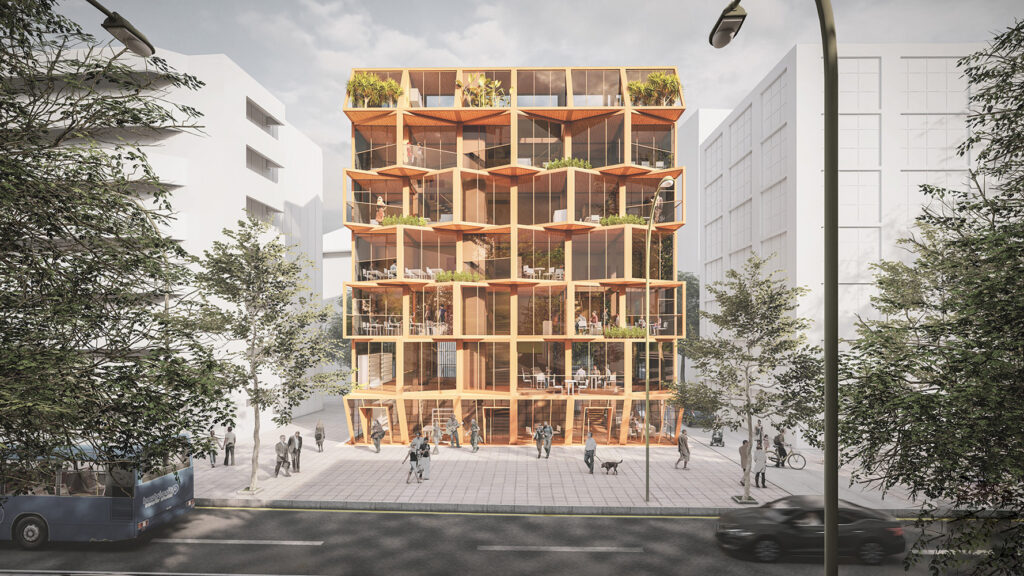
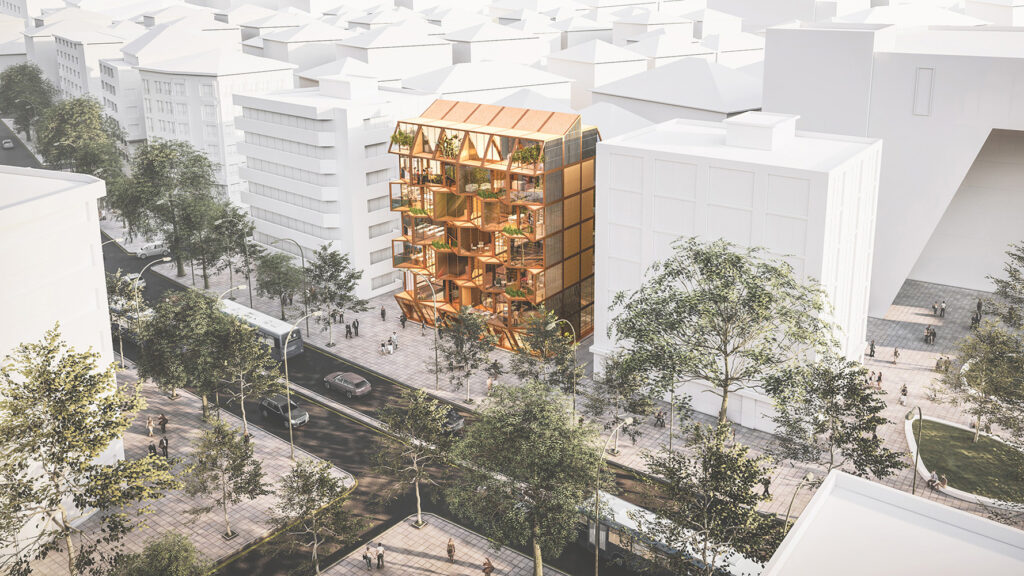
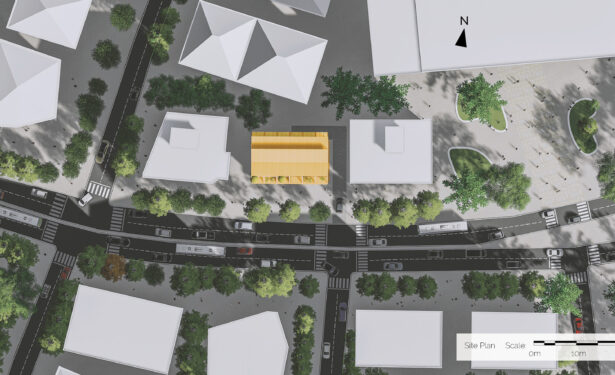
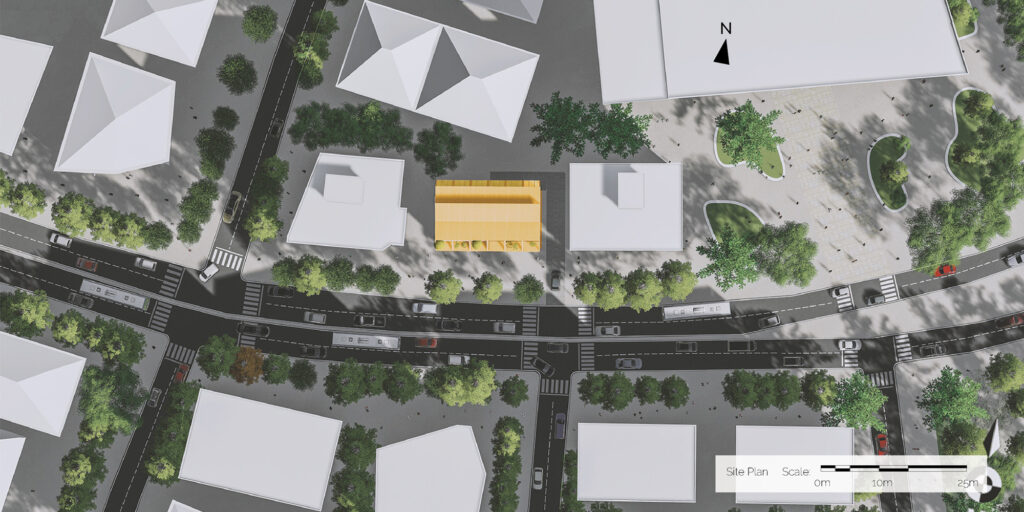
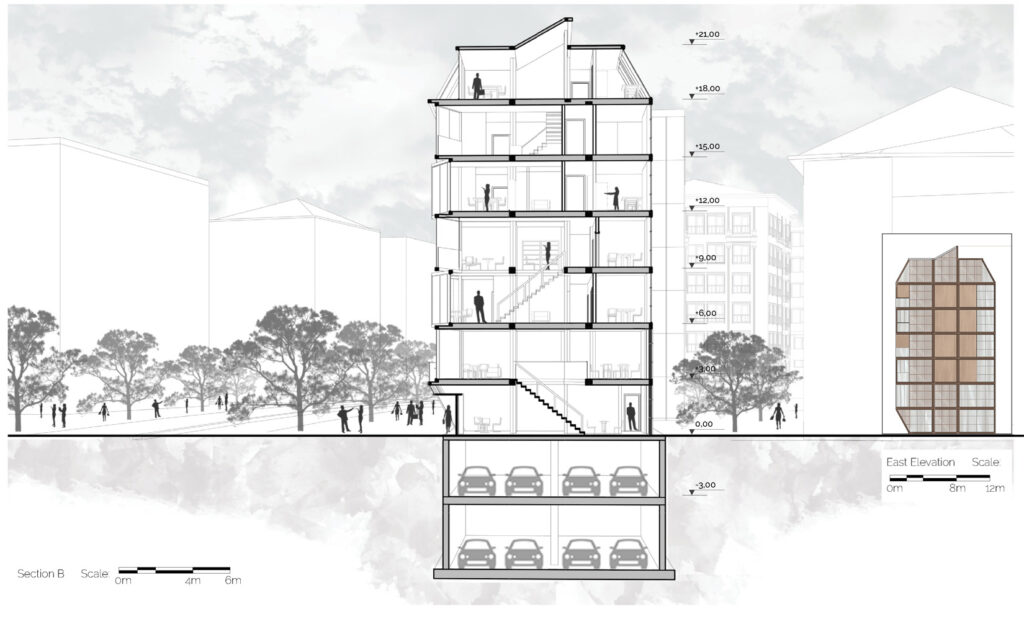
The project site is located in Kızılay, Ankara, Turkey. Kızılay is the center of Ankara, where commercial, cultural and accommodation usage are observed all together. Rapidly changing city centers requires adaptable, low-cost, energy efficient and sustainable solutions for changing spatial needs of the community.
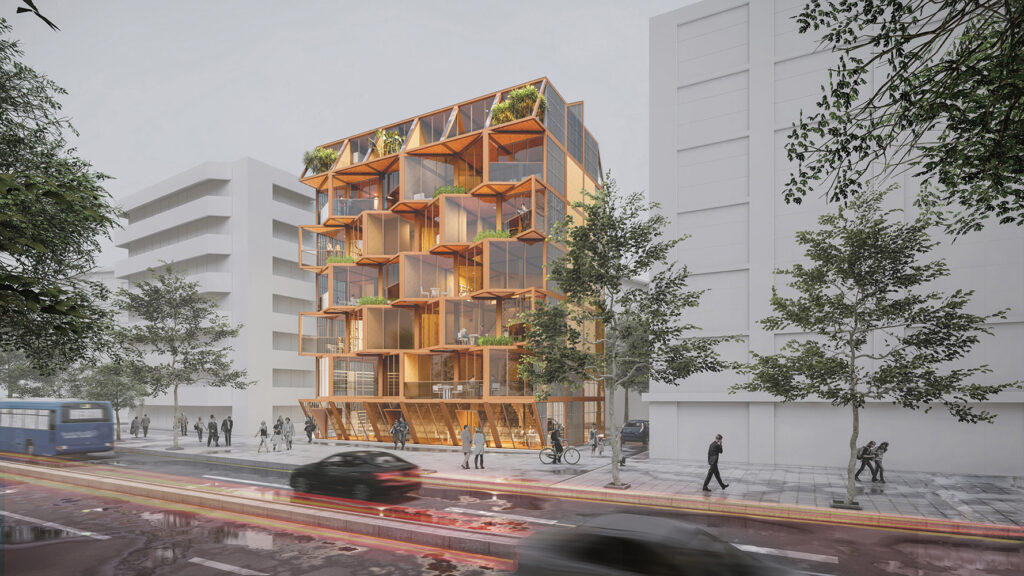
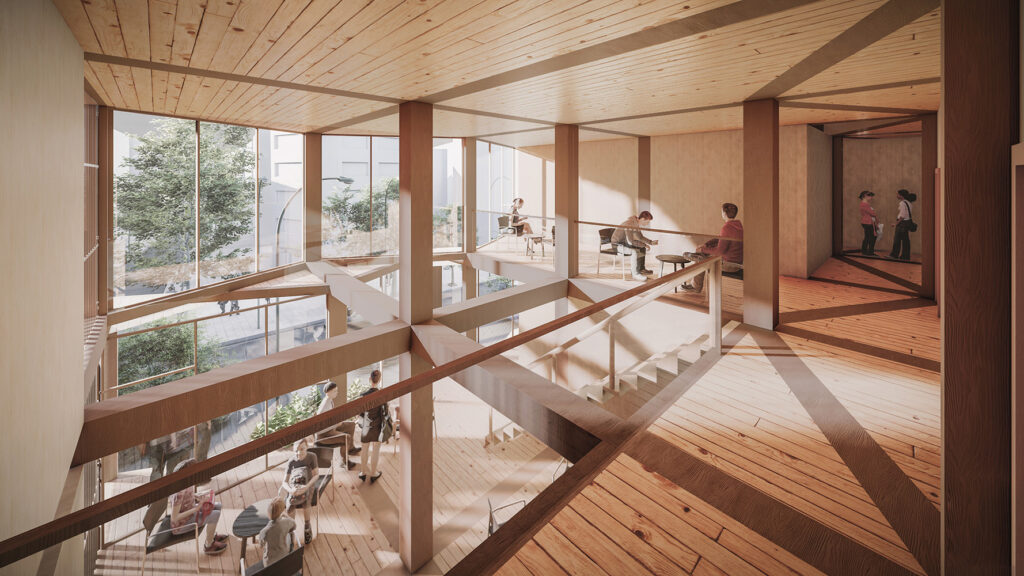
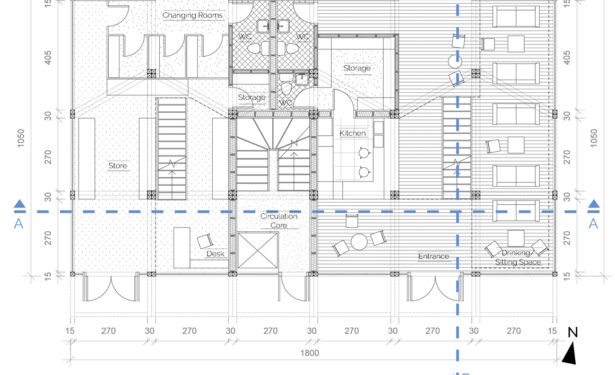
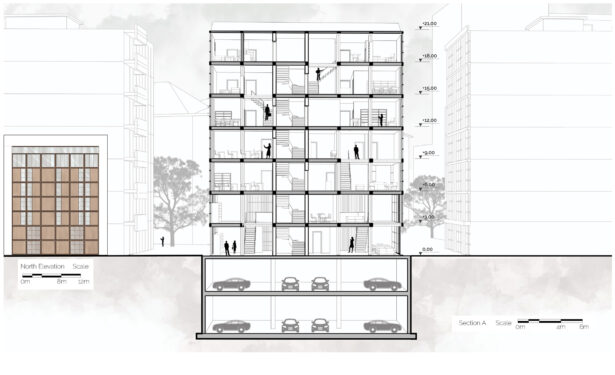
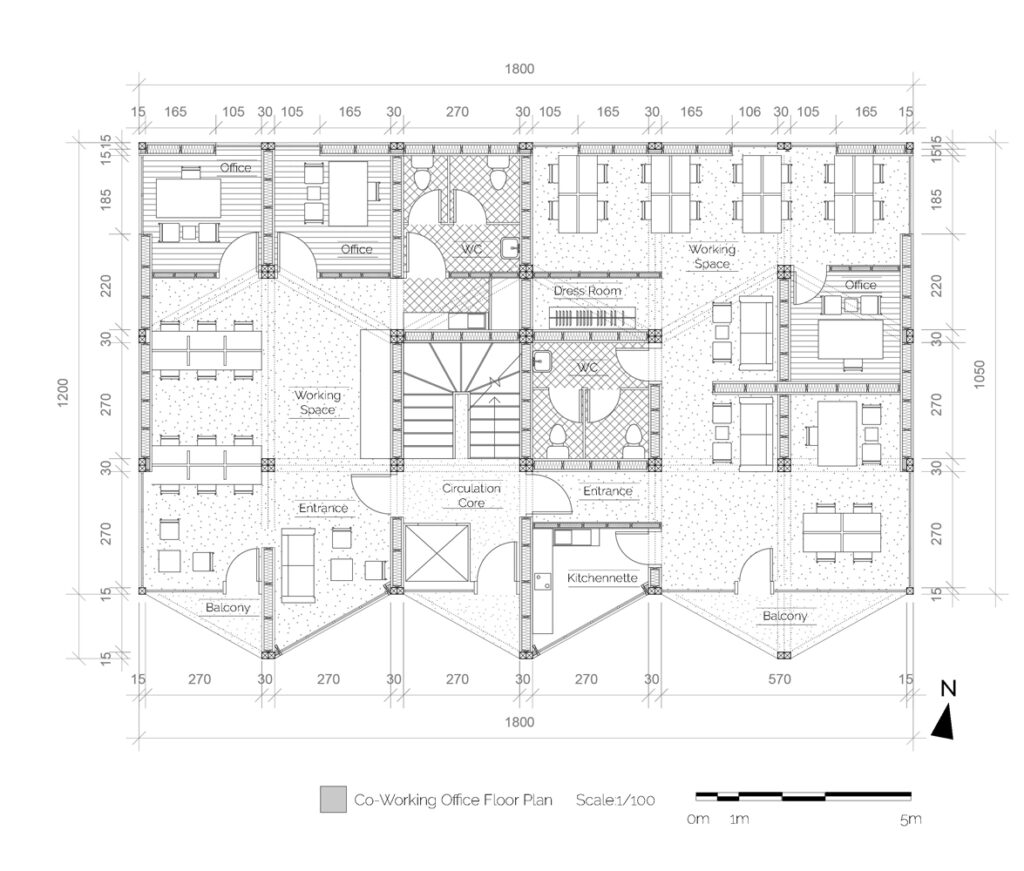
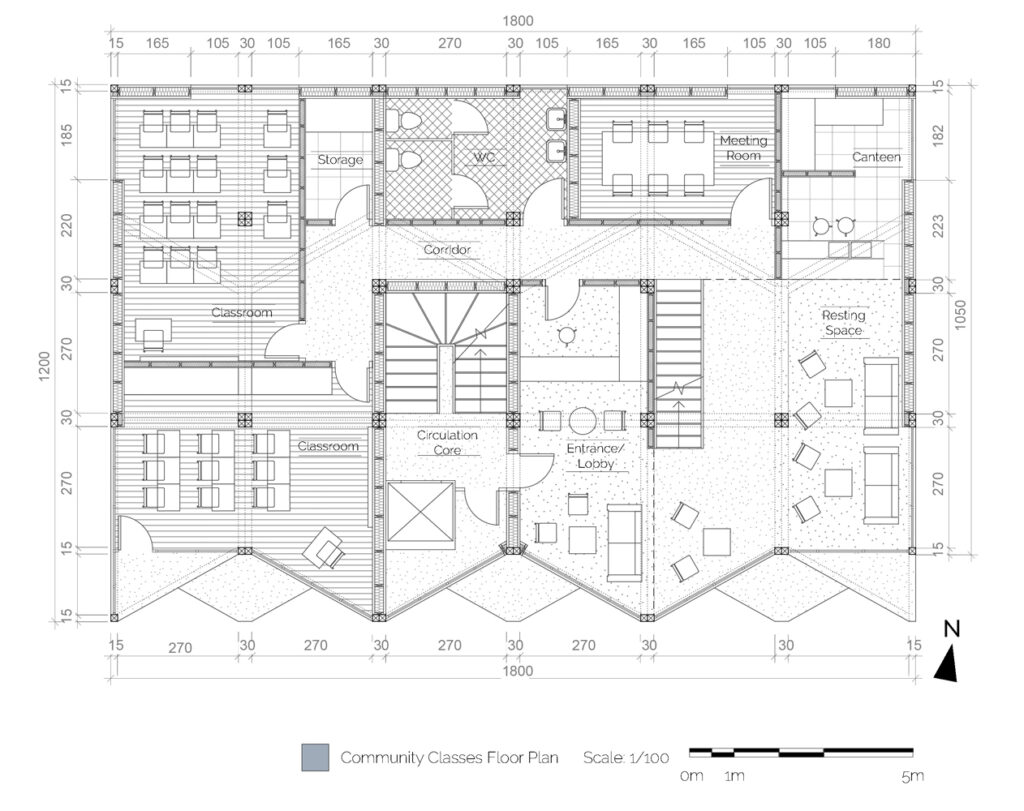
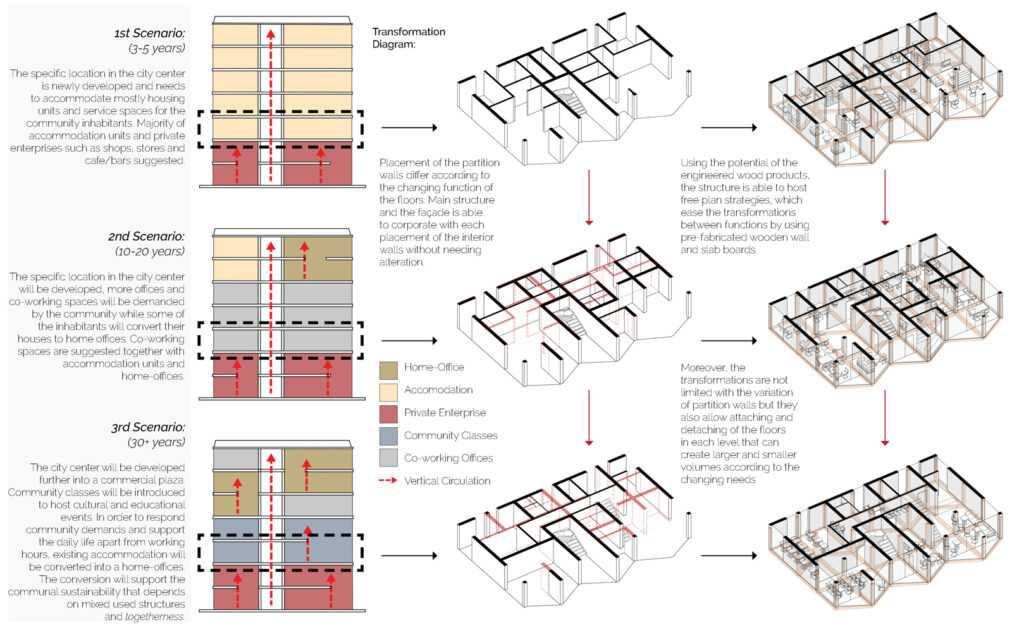
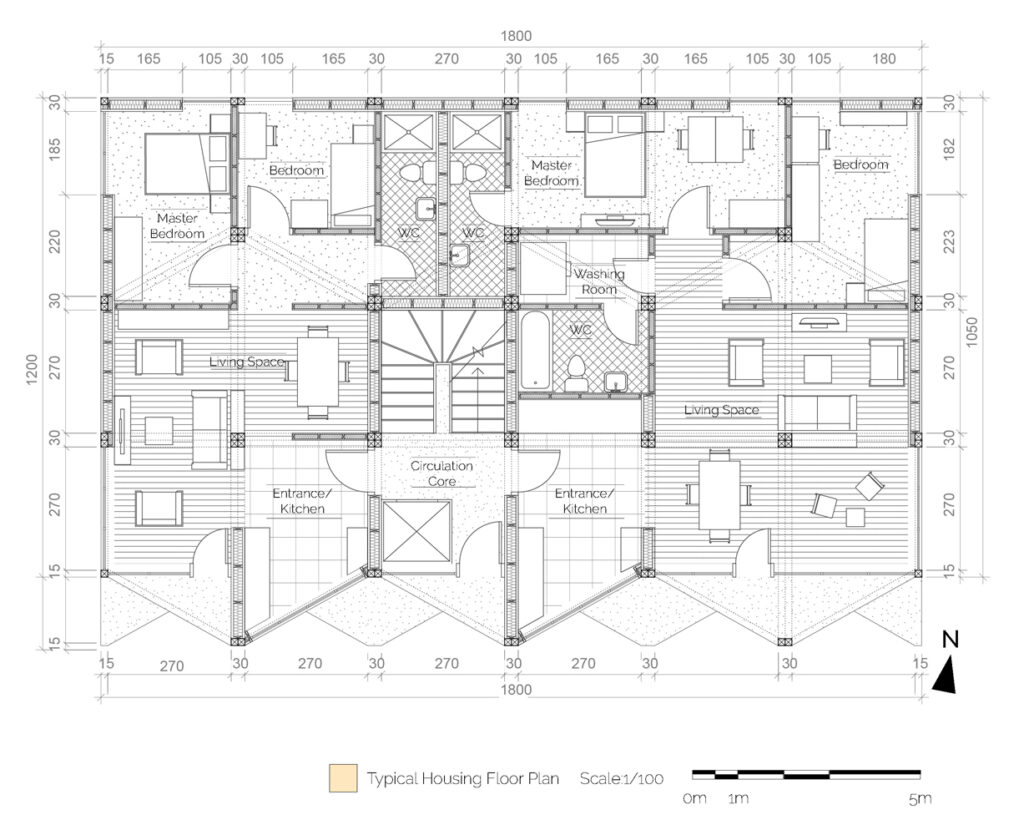
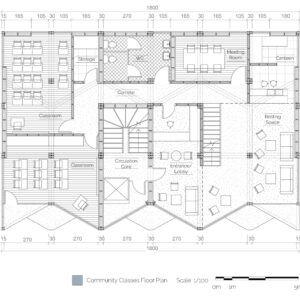
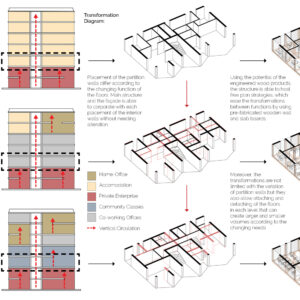
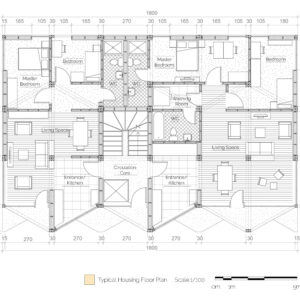
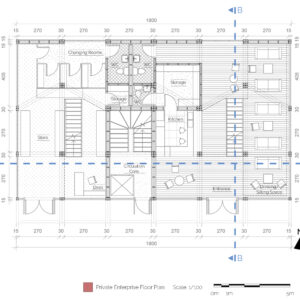
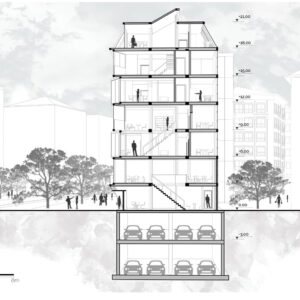
We offer an adaptable structure that accommodates various functions within itself. In time, with the changing needs of the society, the offered structure is able to adapt (but not limited to) predetermined plan types of housing, co-working, public served community classes and private enterprises. These plan types are reproducible and convertible among each floor without the necessity of altering the main structure and the façade but only require adjustments of easily attachable/detachable interior partition walls and floors. This sort of adaptation provides a continuous response to the changing needs of the community by enabling sustainable, low-cost, fast and effective urban adaptation.
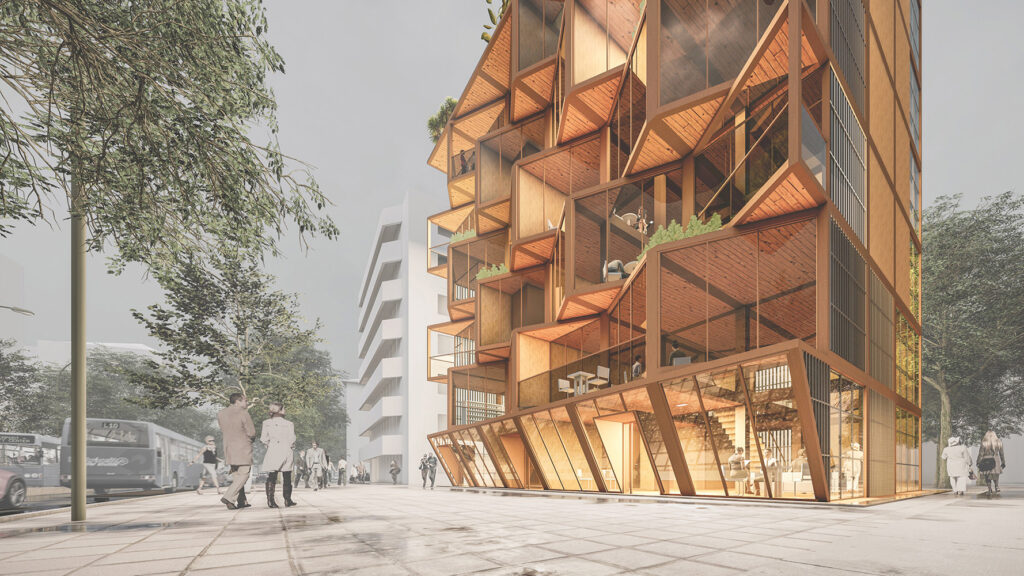
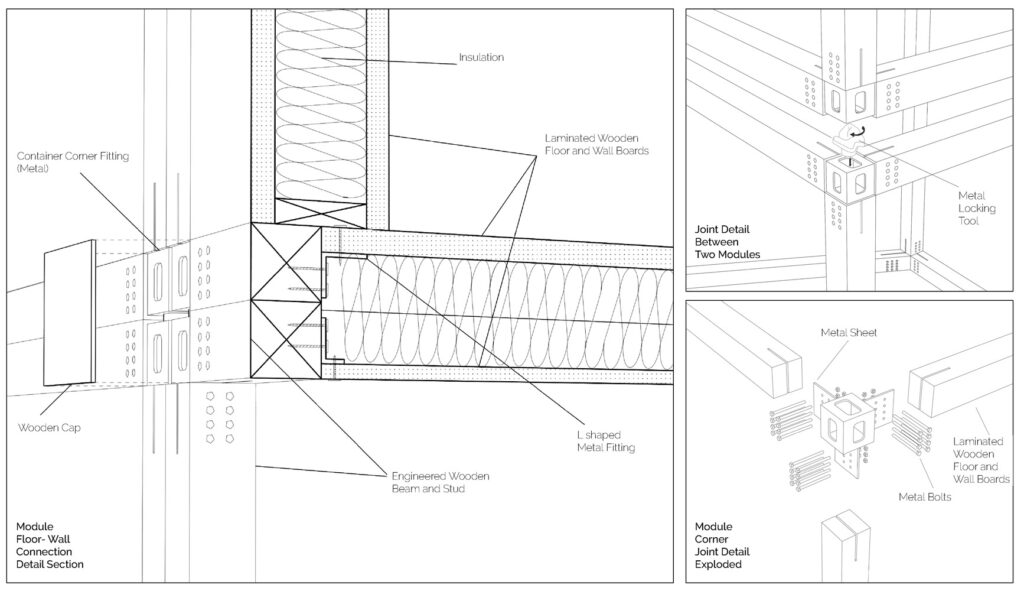
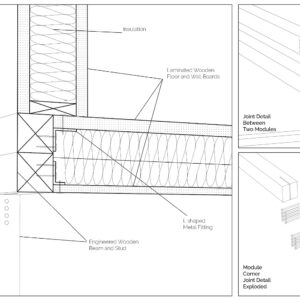
Contrasting to conventional structural material concrete, wood products are obtained from sustainable resources. Also, unlike neighborhood’s reinforced concrete structures, application of the wooden construction system has more advantages in daily use since it reduces the energy consumption for climate resilience with its low thermal conductivity value, which also results in lowering the carbon emission, and in long term, leads to a sustainable and energy efficient community. [1]
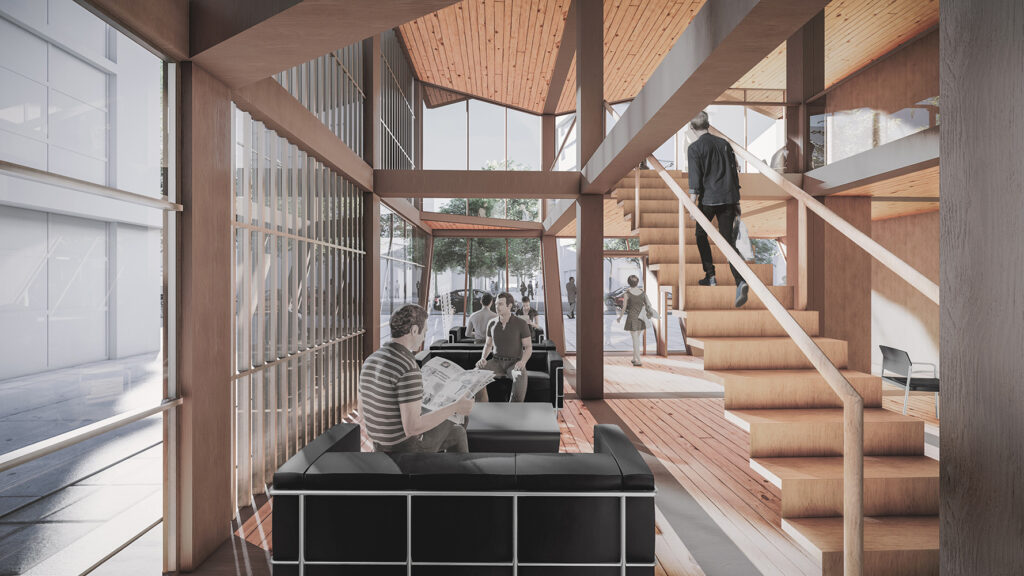
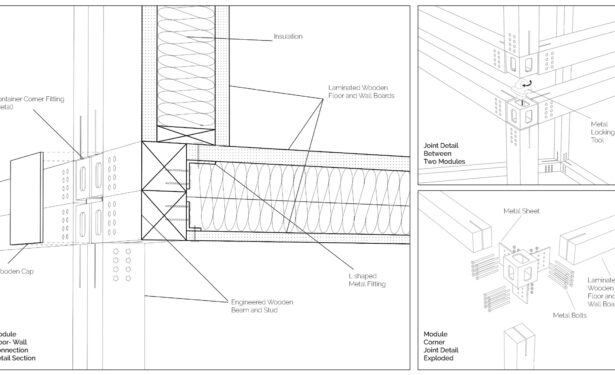
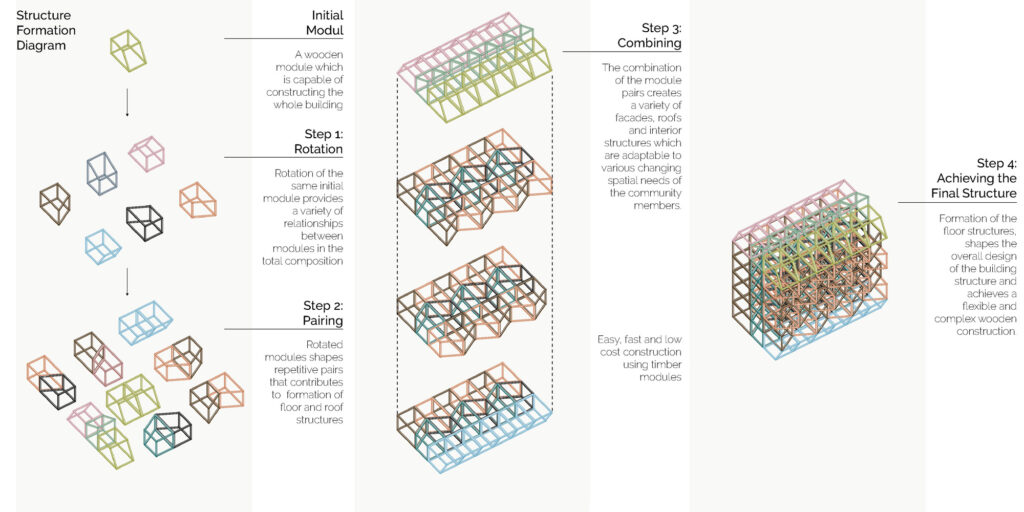
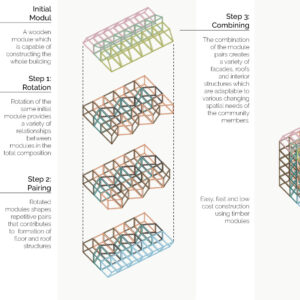
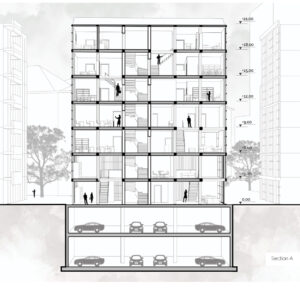
Using a modular wooden construction technique, necessary volumes are created by rotating a simple initial module. Repetition and combination of the same module in various rotations allows creating the structure of interior and exterior volumes, façades and the roof. The rotation creates inclined surfaces for the roof to increase climate resilience, angled balconies in the upper floors to give visual connections to city life and a welcoming entrance in the ground floor facade in order to strengthen the relationship between the building and the main street in ground level. Besides environmental sustainability, these relations are created to host “meaningful involvement” of people to the offered building programs and city life and enhance human relations in the society to achieve social sustainability. [2]
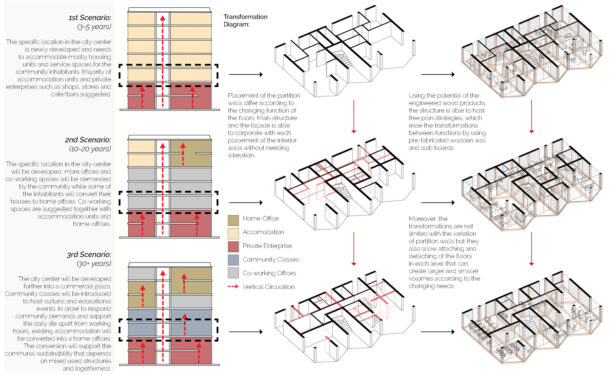
Changing city conditions of Kızılay requires the city center to host less accommodation spaces and more offices and cultural spaces day by day. Three distinct scenarios are offered for the suggested structure’s life cycle in a time range. Altering transformations of the building space and its function are represented as solutions to rapidly changing spatial needs of Kızılay. These solutions include a functional diversity in order to create a heterogeneity of functional usage which will lead to a sustainable city life that meets various needs of the habitants.[3]